Back pain is a common and common health problem in our daily lives. Not only does it affect quality of life, but it also causes many people to miss work, halt physical activities, and can lead to other serious health problems. So for many people, finding ways to reduce pain and prevent back pain is crucial to improving quality of life.
In this blog post, we'll learn about the causes and symptoms of back pain, along with effective treatments and preventions to help you live a healthy and pain-free life. Please.
What is back pain?

Back pain is an uncomfortable, painful or numb condition in the back area, especially lower back pain and upper back pain of the body. In addition, the pain can spread to the hips and legs, and activities such as bending, turning, lifting heavy objects, standing or walking can also make back pain worse.
It can appear at any age and affects many people worldwide. Symptoms of back pain can vary from mild pain to severe pain and can last for a long time.
Is back pain dangerous?
Many people worry that the problem could jeopardize their health. In fact, in most cases, back pain is not a serious problem and usually resolves on its own within a few days or weeks. However, if left for a long time or without proper care, back pain can lead to more serious problems such as neuritis, spondylosis, disc herniation or ischemia of the spine.
Therefore, if you suffer from back pain, it is advisable to find out the root cause of the problem and, if necessary, see a doctor for timely advice and treatment. In addition, there are some good habits to prevent back pain, including exercising regularly, maintaining the correct sitting position when working, and choosing the right bed to support your spine.
Some common symptoms
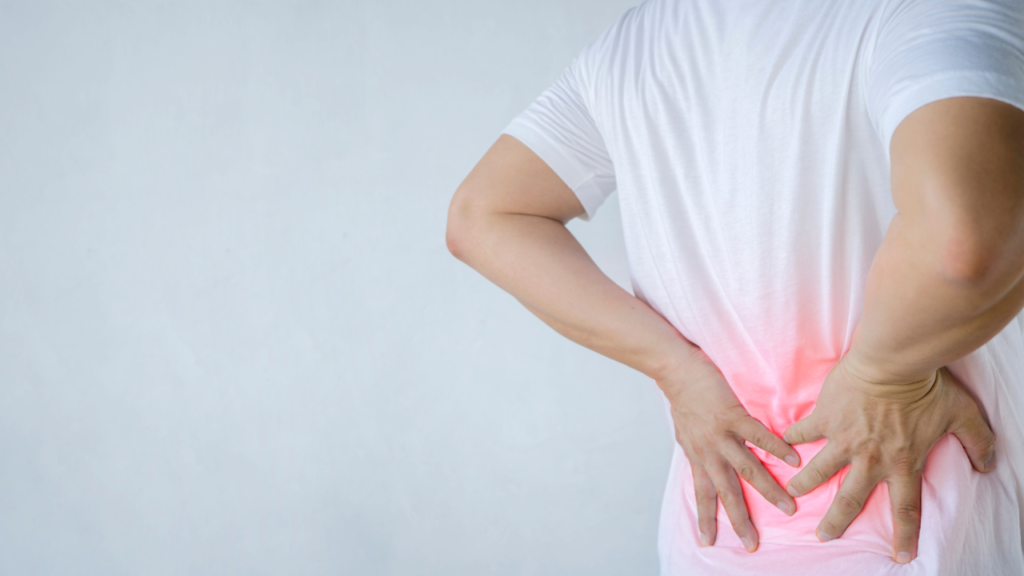
The main symptom of this condition is pain anywhere in the back and sometimes extending down to the buttocks and legs. Some back problems can cause pain in other parts of the body, depending on the nerves affected. Often the pain goes away on its own without treatment. However, if it is accompanied by any of the following symptoms, you should contact your doctor:
- Inflammation or swelling in the back.
- Persistent back pain that resting or lying down does not help.
- Pain down the leg, pain radiating below the knee.
- Urinary incontinence, dysuria, loss of bowel control.
- Numbness or numbness around the genital area or around the anus.
Causes of back pain
The human back is composed of a complex structure consisting of muscles, ligaments, tendons, discs, and bones, all of which work together to support the body and enable movement.
Problems with any of these components can lead to back pain. However, in some cases of back pain, the cause remains unclear. Injury can arise from stress, medical conditions or poor posture, and many other causes.
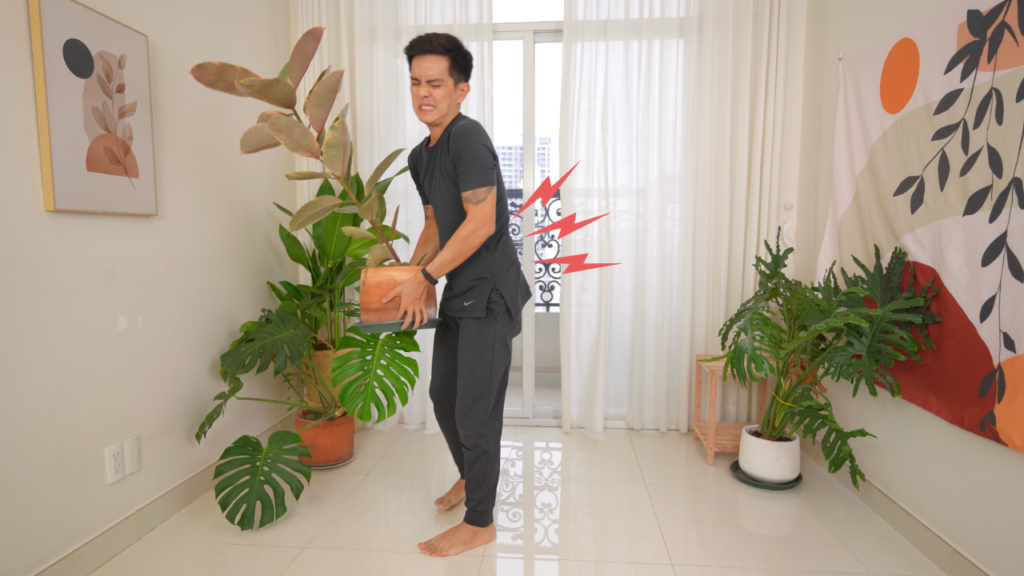

Injury or excessive muscle strain
- Muscles or ligaments are strained
- Damaged disc, herniated disc
- Injury, fracture or fall.
- Lifting something improperly.
- Lift something that's too heavy.
- Make a sudden, hard-to-handle movement.
Some structural problems
Disc problem
- Broken disc: Each vertebra in the spine is cushioned by discs. If the disc ruptures, there is more pressure on the nerve, causing pain.
- Convex anterior disc: Similar to a ruptured disc, a bulging anterior disc can also lead to more pressure on the nerve.
Back spine problems
- Back hammock: When the back is sagged, it will increase pressure on the lower back, which in turn leads to back pain and back pain.
- Humpbacked: Hunchback can cause back pain by creating pressure and strain on the spine and surrounding muscles, leading to body imbalance and back pain.
- Flexed vertebrae: If the spine bends abnormally, back pain may occur. An example of this is scoliosis, in which the spine curves to the side.
Some other structural problems
- Sciatica pain: The pain was sharp to the buttock and down along the thigh. This can happen when a bulging or ruptured anterior disc presses on a nerve or when a particular muscle presses on the sciatic nerve.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can cause problems with joints in the hips, lower back, and other areas of the body. In some cases, the space around the spinal cord shrinks. Medical professionals call this spinal stenosis.
- Osteoporosis
- Kidney problems: Kidney stones or a kidney infection can cause back pain.
Habits of movement and posture
Back pain can also be caused by some routine activities or poor posture, for example:
- Habit of turning and twisting
- Excessive stretching of the body
- Bowing for a long time
- Push, pull, lift or carry something
- Standing or sitting for long periods of time
- Stress the neck forward, for example when driving or using a computer
- Sleep on a mattress that does not support the body or keep the spine straight.
Other causes
- Cauda equina syndrome: The cauda equina is a bundle of spinal nerve roots that arise from the terminal end of the spinal cord. Symptoms of this syndrome include sharp pain in the lower back and upper buttocks along with numbness in the buttocks, genitals, and thighs. Occasionally, bowel and bladder dysfunction also occurs.
- Spine cancer: Tumors on the spine can compress nerves, causing back pain. Structural damage to the bone can also be painful in the presence of a tumor or metastasis to the bone.
- Spinal infections: Fever and warm, tender areas of the back can be caused by a spinal infection.
- Other infections: Pelvic inflammatory disease and kidney or bladder infections can also cause back pain.
- Sleep disorders: People with sleep disorders are more likely to experience pain than others.
- Visceral perforation: A type of bacterial infection can affect nerves, causing back pain. Depending on which nerves are affected, darkening of the skin may be accompanied by back pain.
A popular treatment
Note: Back pain is usually resolved with rest and self-healing measures, but sometimes medical treatment is required.
Drug treatment
If home remedies don't relieve back pain, your doctor may recommend medications or physical therapy. For this method, you must use the drug according to the instructions of the doctor and note the side effects to avoid unnecessary complications.
Physiotherapy, sports training
- Use heat, cold, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation as well as some muscle release techniques to relieve pain.
- A physical therapist can recommend a number of exercises that increase flexibility and strength for the back and abdominal muscles.
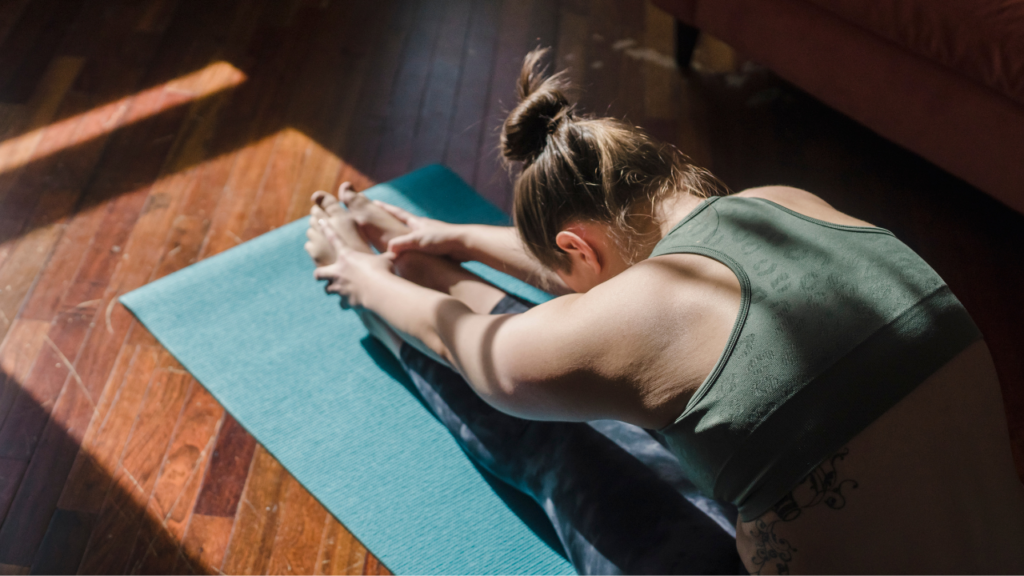

- Practice the moves Yoga therapy or Pilates: Yoga or Pilates exercises help strengthen the spine and relieve back pain.
- Exercise: Exercise regularly to keep muscles and joints healthy and reduce stress and tension.
Change your daily routine
- Keep your weight balanced: Keep your weight at a stable level and avoid gaining weight too quickly to reduce pressure on the spine.
- Eat healthy and lose weight.
- Change sitting and standing positions: Try to change standing and sitting positions often, especially if you have to sit for a long time or use the computer often.
- Use a back cushion: Use a back cushion when sitting to keep your back supported and reduce pressure on your spine.
- Change the bed: Choose the right bed and lie in the right position.
- Focus on your back when lifting heavy: When lifting heavy objects, use your thighs and leg muscles to relieve pressure on the spine.
Nguyen hopes that the above sharing will be effective and useful for your situation. Besides, there are also many articles on health and yoga therapy at Nguyen's blog, especially Youtube channel Nguyen has many other useful exercises and movements, please follow and look forward to Nguyen!
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/172943
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/back-pain/



